Understanding pump curves is essential for selecting and operating Seepex pumps effectively. These curves provide critical information on performance and help you make informed decisions regarding pump applications.
What Are Pump Curves?
Pump curves graphically represent the relationship between various performance parameters of a pump, such as:
- Flow Rate (Q): The volume of fluid the pump can move per unit time (usually in gallons per minute or liters per second).
- Head (H): The height to which the pump can raise the fluid (measured in meters or feet).
- Efficiency: The effectiveness of the pump in converting input power to hydraulic power.
- Power Consumption: The amount of energy required to operate the pump.
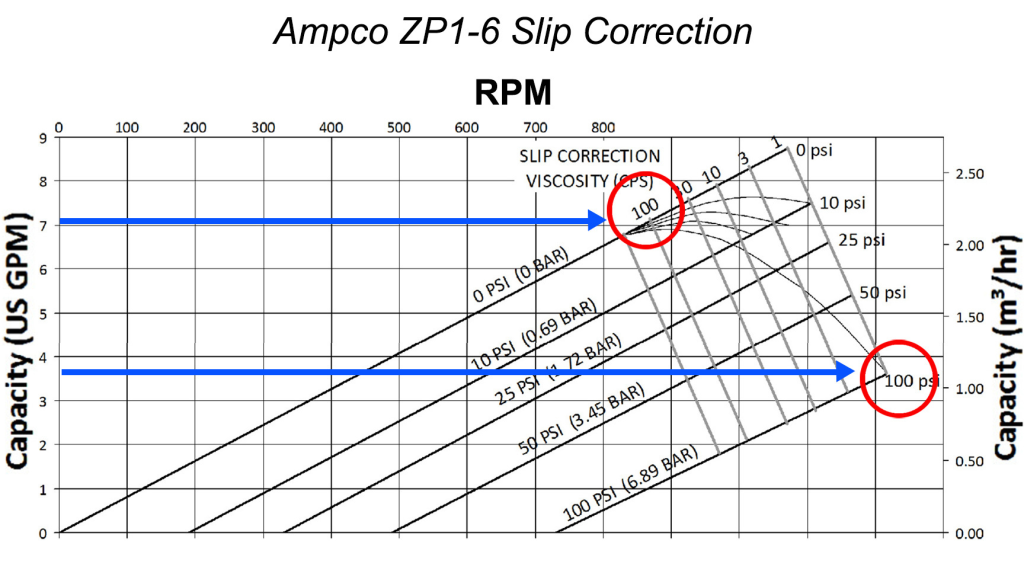
Step-by-Step Guide to Reading Seepex Pump Curves
- Identify the Type of Curve:
- Seepex provides different curves for various pump models. Ensure you are looking at the correct curve for your specific pump type.
- Locate the Flow Rate (X-Axis):
- The horizontal axis typically represents the flow rate. Identify the scale to determine the flow rates relevant to your application.
- Find the Head (Y-Axis):
- The vertical axis usually indicates the head (pressure) produced by the pump. This is vital for understanding how high the pump can lift the fluid.
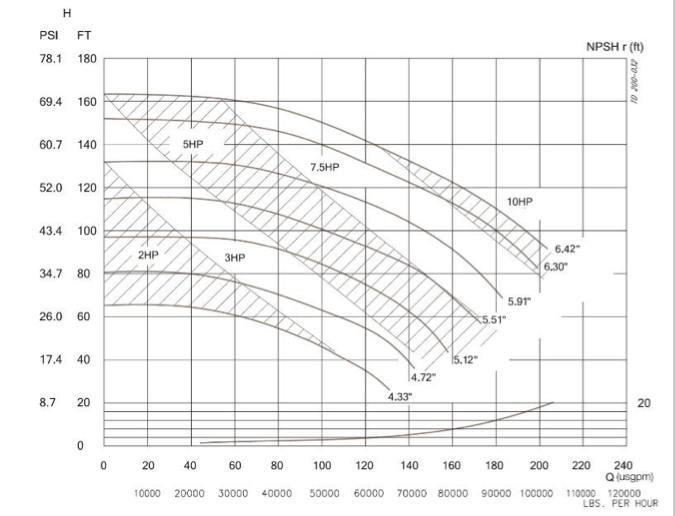
- Examine the Performance Lines:
- Pump Performance Curve: This line shows how the head decreases as the flow rate increases.
- Best Efficiency Point (BEP): Look for the point on the curve where the pump operates at its highest efficiency. It is crucial to operate close to this point for optimal performance.
- Understand the Efficiency Curve:
- Often shown as a series of curves on the same graph, these lines indicate the pump’s efficiency at different flow rates. Higher efficiency means lower operating costs.
- Review the Power Consumption Curve:
- This curve indicates how much power the pump requires at different flow rates. It helps in understanding energy costs associated with pump operation.
- Check for NPSH Requirements:
- Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) curves show the minimum pressure required at the pump inlet to prevent cavitation. Ensure your system provides sufficient NPSH for reliable operation.
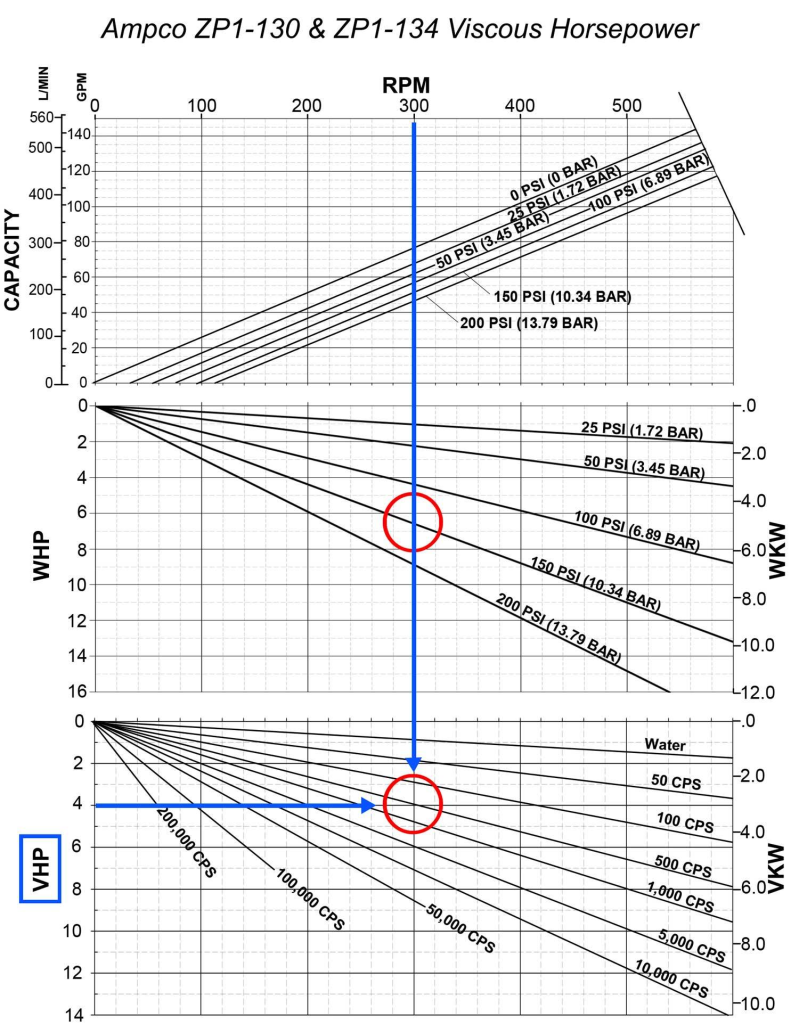
- Consider the Application:
- Match the pump curve characteristics with your application requirements such as fluid type, temperature, viscosity, and specific system demands.
Conclusion
Reading and understanding Seepex pump curves is essential for optimal pump selection and operation. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can make informed decisions that enhance pump performance, efficiency, and longevity, ultimately leading to cost savings in your operations. Always consult the specific pump curve for your model to ensure accurate data interpretation and application suitability.